Khuôn đa thành phần
Khuôn đa thành phần
Trong việc ép phun đa thành phần (còn được gọi là sản xuất phun nhiều màu-ghi chú của người dịch), các loại nhựa hoặc nhựa khác nhau có màu khác nhau được sử dụng để tạo ra các sản phẩm đúc phun thông qua các quy trình khác nhau.
Trong những năm gần đây, với sự mở rộng liên tục của các trường ứng dụng, công nghệ ép phun đa thành phần đã ngày càng trở nên quan trọng. Các giải pháp sáng tạo luôn thay đổi làm cho việc ép phun đa thành phần ngày càng hấp dẫn trên thị trường đang phát triển.
Một trong những lý do chính cho sự phát triển nhanh chóng của công nghệ đa thành phần là lợi ích tiềm năng mang lại do giảm các bước sản xuất. Bằng cách áp dụng công nghệ khuôn tiên tiến, cả quy trình lắp ráp thủ công và tự động của các sản phẩm có thể được hoàn thành trong khuôn. Từ quan điểm của thiết kế sản phẩm, công nghệ ép phun đa thành phần là hấp dẫn trong việc ngăn chặn vi phạm bản quyền thiết kế và sản phẩm phụ với các hiệu ứng xúc giác tốt hơn.
1. Công nghệ DSLIDER (Công nghệ rút lại cốt lõi)
Ưu điểm lớn nhất của quá trình này nằm ở lựa chọn linh hoạt của vị trí của đầu vào thành phần thứ hai. Chỉ khi thanh trượt trong khoang của phần prastic hóa (i .e., Thành phần nhựa đầu tiên-Lưu ý của người dịch) mới được rút ra, nhựa thứ hai có thể đi vào không gian được giải phóng trong phần trước.
Bằng cách sử dụng công nghệ rút lại cốt lõi, các sản phẩm được kết nối chặt chẽ có thể được sản xuất với các kết hợp vật liệu tương thích. Đó là, trước khi chữa khỏi thành phần đầu tiên, vật liệu thành phần thứ hai được tiêm và khuôn không cần phải di chuyển hoặc mở.
Do kết nối nhanh chóng trong quá trình ép phun, kết nối giữa hai thành phần trong sản phẩm rất đồng đều, trong khi sự xen kẽ chặt chẽ của hình dạng hình học đạt được bằng thành phần thứ hai. Ở trạng thái nóng chảy, thành phần thứ hai của nhựa có thể dễ dàng thấm vào các khoảng trống của thành phần đầu tiên. Công nghệ này là cả đơn giản và tiết kiệm không gian.
Bởi vì việc ép phun song song không thể đạt được trong quá trình rút lại lõi, thời gian ép phun của hai vật liệu được chồng lên nhau. Đúc tuần tự của các thành phần khác nhau làm tăng tổng chu kỳ đúc. Do nhược điểm này, phương pháp rollback cốt lõi đã được sử dụng ngày càng ít hơn.
2. Quy trình ép phun (chuyển tay cơ học)
Chuyển đúc phun được sử dụng khi các bộ phận đúc phun cần phải được vượt quá. Các vị trí để đúc trước và đúc phun cuối cùng có thể được sắp xếp trái và phải hoặc lên xuống. Các tay cơ học chuyển các bộ phận trước nhựa và lấy các sản phẩm hoàn chỉnh.
Tương tự như quá trình rút lại cốt lõi, loại khuôn này không yêu cầu hành động quay, vì vậy cấu trúc của nó không phức tạp. Ưu điểm của nó là hai vật liệu có thể được phun đồng thời. So với phương pháp rút lại cốt lõi, nó sẽ rút ngắn đáng kể chu kỳ đúc.
Quá trình ép phun chuyển cũng bao gồm: đúc trước một sản phẩm nhất định trên một máy, sau đó loại bỏ phần đúc sẵn này và hoàn thành việc ép phun bằng vật liệu khác trên máy khác.
Độ tin cậy của quá trình nhúng các bộ phận tiền sinh vào một khoang khác là vô cùng quan trọng. Quá trình điều chỉnh bàn tay cơ học dựa trên kinh nghiệm là khá phức tạp. Một thiết bị tay cơ học chính xác và có thể điều khiển là cần thiết để đảm bảo định vị chính xác của các bộ phận trước nhựa tại trạm cuối cùng.
Quá trình ép phun chuyển sử dụng đầy đủ khu vực của bảng khuôn hiện tại, nhưng nó không phù hợp để sản xuất các bộ phận đúc phun với hình học rất tốt.
Khuôn đúc Ô Tô Công ty TNHH khuôn đúc jiefeng thái Châu (jfmoulds.com)
3. Khuôn mốc tấm
Tấm phân chia được tích hợp trên mẫu di chuyển và có thể xoay. Sau khi khuôn được mở, tấm phân chia chuyển phần được đúc sẵn sang trạm tiếp theo của khuôn, và sản phẩm cuối cùng được đúc.
Một mẫu có thể xoay thứ ba đã được thêm vào hai mẫu của khuôn tấm phân chia. Tấm này có thể xoay quanh trục trung tâm. Tấm phân chia được đẩy ra đầu tiên và được giải phóng khỏi phía di chuyển, sau đó xoay quanh trục trung tâm đến vị trí thứ hai. Chuyển động quay được điều khiển bởi giá đỡ được điều khiển bởi động cơ thủy lực hoặc động cơ servo, và độ chính xác của nó có thể đạt hàng chục micron.
Sau khi tấm phân chia tăng lên, xoay và rơi trở lại, lõi sẽ trở về vị trí ban đầu của nó trong khuôn di chuyển. Sau đó, khuôn đóng lại và chu kỳ ép phun tiếp theo bắt đầu. Tại trạm thứ hai, phần trước nhựa được nhúng với một thành phần khác của nhựa.
Vòng quay của tấm phân chia có thể là 2 × 180 ° hoặc 3 × 120 °. Trạm thứ ba thường được sử dụng để làm mát hoặc loại bỏ các bộ phận đúc phun. Người chạy nóng được sử dụng rất hạn chế trong phân chia khuôn tấm.
4. Khuôn hỗ trợ trung tâm
Hệ thống stent trung tâm tương tự như công nghệ tấm lập chỉ mục. Các tấm phân chia có thể được đơn giản hóa thành một tấm dải dài hoặc hình chữ thập. Hỗ trợ trung tâm chỉ quay phần đúc phun sang trạm tiếp theo mà không xoay bất kỳ thành phần cơ học nào của khuôn. Các bộ phận đúc phun được cố định bằng các lõi có thể mở rộng, ghim đẩy hoặc pawl trong quá trình chuyển.
Tấm phân chia được thảo luận trước đó đã được đơn giản hóa thành một hỗ trợ trung tâm xoay quanh phần đúc phun và sau đó tiến hành đúc phun. Các khuôn giàn giáo trung tâm thường sử dụng các hệ thống chạy chạy nóng. Một lợi thế của nó so với hệ thống tấm lập chỉ mục là trọng lượng tự trọng của hệ thống quay nhỏ hơn, cho phép nó xoay hoặc xoay nhanh, do đó làm giảm đáng kể chu kỳ hình thành của hệ thống.
Việc đúc các bộ phận đúc phun có thể được thực hiện bằng phía tiêm hoặc phía phóng. Nó được nắm bắt bởi một lõi kính thiên văn trong quá trình dịch chuyển và sau đó được đẩy ra từ một lỗ trung tâm.
5. Hệ thống bàn xoay
Multi-component molds using turntable systems have been widely applied in various fields of the plastic industry. Depending on different application scenarios, the turntable can be driven by hydraulic power or a motor. Using a turntable system is the most effective solution for the mold to rotate from one injection position to the next. The rotation of the mold is accomplished by the turntable, making the mold simpler.
Depending on the number of injection molding components, the positioning of the turntable can be divided into 4×90°, 3X120° or 2X180°. Among them, the simplest is to rotate the turntable 180° to the left or right. The feature that the moving die can rotate continuously in one direction is particularly suitable for multi-station molds. As the mold needs to rotate continuously, cables and
The connection of hoses, the supply of cooling water and hydraulic oil will become quite complicated.
Compared with other multi-component molds, one drawback of the turntable system is that it requires a larger injection molding machine. Generally, the length of the machine guide rails in a turntable system needs to be increased by 200mm, and the distance between the guide rails needs to be increased by 50 to 100mm.
6.bucket lifting mold
In a broad sense, the working mode of bucket lift molds and transfer injection molding technology is similar. The production is transferred from an integrated screw mechanism to the next injection molding station.
The highlight of this mold technology is that the multi-component injection molding machine used does not require special specifications. The mold will be slightly longer than the rotating mold, but it doesn't need to be rotated. In this way, there is no need to enlarge the template or increase the length of the guide pins of the injection molding machine.
The pre-molded part is moved to the next station through a screw. Then, the product undergoes injection molding and is transferred to the unloading station outside the mold. The mechanical hand takes down the finished product during the injection molding stage, and the injection molding cycle will not be affected.
The empty half mold is sent back to the injection molding station again. During the mold opening stage, the second screw moves the half mold from the unloading station to the pre-plasticizing station. In this way, the bucket lifting cycle is completed and a new cycle begins anew.
Khuôn đúc hàng hóa Công ty TNHH khuôn đúc jiefeng (jfmoulds.com)
7-cubic-meter stacked mold technology
The advantage of cubic mold stacking technology over other mold technologies lies in the fact that with the same size of machine, the number of cavities in the mold can be doubled. In other words, for the same order volume, the size of the machine can almost be halved.
7.1 Cubic rotary mold stacking technology
When applying the rotary die stacking technology, the rotation of the mold is accomplished by a horizontally rotatable central module.
The pre-plastic part is first formed on the first parting surface. When the mold is opened, the pre-plastic part remains on the central rotating module. When the mold is fully opened, the central module rotates 180° to the second profile surface. After the mold is closed again, the second component of the plastic is injected into the second cavity containing the pre-molded part.
By applying a 4×90° rotating cubic die, secondary processing can be carried out simultaneously at the second station (operator side) and the fourth station (non-operator side). For instance, the second station is used for cooling injection-molded parts, while the fourth station is for the mechanical hand to pick up the products. The two processes are carried out simultaneously without affecting the molding cycle
Impact. Alternatively, the second station can also be used for in-machine or out-of-machine assembly (in-mold assembly).
7.2 Double Cubic rotating Die Stacking Technology
The double cubic stacked mold is placed between the moving and fixed half molds, and two sets of rotating stacked molds are also configured. In principle, a double-cubic stacked mold is like two independent molds working simultaneously. It has three clamping surfaces and all forming processes are carried out simultaneously, which makes the production of complex parts highly efficient.
Compared with traditional molds, when the assembly process needs to be transferred to the mold, the double cubic stack mold has a significant advantage, and the molding cycle will also be greatly reduced. Assembly processing can be carried out simultaneously with injection molding. More and more assembly processes have been transferred to in-mold operation. Because the products assembled in the mold have higher precision.
The preferred application fields of double cubic stacked molds include packaging, medical care and the automotive industry. With one process, the integration of two or more packaging components can be achieved.
8. Sequential mold stacking
Sequential mold stacking involves two sets of molds being connected back to back, with plastic filling each mold cavity in sequence and the molds being opened in a cycle.
In a common mold, the cavities on the parting surface stand opposite to each other. They are filled simultaneously during each injection molding, and the finished products are demolded at the same time when the mold is opened.
However, in sequential die stacking, the parting surfaces open alternately. That is to say, when half of the mold cools down, the other half of the mold is just demolded and re-injected. During the idle time of mold cooling, the next injection molding stage can be carried out. When the two semi-molds work in sequence, different injection molded parts of the same product series can be produced. Therefore, injection molding machines must be equipped with special programs to provide the appropriate amount of plastic required for each parting surface.
Thick-walled parts with longer cooling times are also particularly suitable for this technology.
The external edge lock mechanism enables the two semi-molds to operate alternately. The function of the side lock is similar to that of a rack and pinion system. By using a single adapter board, two ready-made molds can be transformed into a set of sequential stacked molds.
9.component molds for thermosetting plastics and elastomers
In thermosetting multi-component molds, thermosetting plastics are rarely paired with thermosetting plastics. In most cases, two types of materials, soft and hard, are used in combination. However, there are also examples of combinations of thermosetting plastics and high-temperature resistant thermoplastic central support rotary process indexing sheet materials.
Elastomers can be combined with thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. In both cases, the pre-molded parts should be made of hard plastic.
The combination of thermosetting plastics and elastomers is mostly used in the field of engines. Both of these plastics have the characteristics of good thermal stability, resistance to engine oil and fuel oil. Therefore, thermosetting plastics and elastomers [usually nitrile rubber (NBR)] with very similar material classifications can be combined very well. The temperatures at which these two materials are produced using heated molds are also at the same level. The difference between them lies in that thermosetting plastics need to be hardened to become elastic
The body needs to be vulcanized.
The combination of soft and hard plastics can be used to improve the sense of touch or absorb vibrations. Examples of improving tactile sensation through the combination of soft and hard plastics include small devices such as hand drills, welding guns or hair dryers. Such a combination can be used in automotive engineering and engine technology to selectively absorb vibrations.
Thông tin liên quan
Khuôn phun thường được sử dụng sáu loại vật liệu khuôn
2025-06-19
Việc lựa chọn thép không chỉ ảnh hưởng đến tuổi thọ của khuôn, mà còn ảnh hưởng đến...
Khám phá Vòng đời đầy đủ của khuôn phun và suy nghĩ về những đột phá trong ngành
2025-07-15
Khám phá Vòng đời đầy đủ của khuôn phun và suy nghĩ về sự phá vỡ ngành công nghiệp...
Thiết kế khuôn đặc biệt
2025-07-24
Thiết kế khuôn đặc biệt1 Mold Stackthe Stacked Fold sản xuất đồng thời sản xuất ...
Xác định khung mẫu mới cho ngành công nghiệp khuôn phun thông qua các đột phá công nghệ và tái tạo sinh thái
2025-07-04
Định nghĩa một mô hình mới cho ngành công nghiệp khuôn phun thông qua công nghệ BREA...
Một bộ sưu tập các quy trình sản xuất khuôn mẫu, tiêu chuẩn, quy trình và vỏ.
2025-06-19
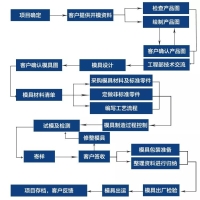
Biểu đồ Lưu lượng quá trình như sau: tất cả các loại công cụ và sản phẩm được sử dụng trong...